Embracing the Value of Blockchain
Blockchain is the latest technology that business executives are exploring as a means to improving business processes. I was introduced to this technology while in business school at Yale and in studying this technology I found several sources which merit special mention: the IBM sponsored Blockchain for Dummies, the Deloitte Debriefs on Blockchain and the Role of the CFO, and the Blockchain Council which has a very informative website at www.Blockchain-council.org
In this article I summarize the plethora of information obtained into the following sections:
- What is Blockchain and Why is it Important?
- Blockchain Benefits
- The Use of Smart Contracts and Integrating Artificial Intelligence
- Vision, Strategy, and Execution
What is Blockchain and Why is it Important
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that allows transactions to be processed immutably and in real time. Rather than having multiple databases, the architecture gives participants the ability to share a distributed ledger that is updated, through peer-to-peer replication, every time a transaction occurs. This connectivity means that each participant (node) acts as both a publisher and a subscriber. Each node can receive or send transactions to other nodes, and the data is synchronized across the network as it is transferred.
Blockchain networks can be private with restricted membership similar to an intranet, or publiclike the Internet, accessible to any person in the world
Blockchain has relevance that go way beyond obvious applications like digital (crypto) currencies and money transfers. Valuable business uses range from electronic voting, smart contracts, digitally recorded property assets, patient health records management, and proof of ownership for digital content.
Blockchain is important to business growth because it overcomes the limitations of current transaction systems which are unable to cope with the explosion of internet-based transactions and the need to improve the convenience, speed, efficiency and underlying trust with counterparties in a global setting. The Blockchain platform addresses the limitations of traditional databases such as:
- Inefficiencies due to the record keeping of multiple ledgers, and the need for extensive third-party validation often involving several intermediaries.
- Fraud, cyberattacks, and even simple mistakes add to the cost and complexity of doing business, and expose all participants in the network to risk if a central system, such as a bank, is compromised.
- Credit card organizations have erected costly barriers to entry and conduct business. Merchants, relying on the traditional credit card system, must pay the high costs of onboarding, which often involves considerable paperwork and a time-consuming vetting process.
- A significant number of people do not have access to a bank account, particularly in developing economies, and have had to develop parallel payment systems to conduct transactions.
Blockchain Benefits
Similar to how the internet changed the world by providing greater access to information, Blockchain is poised to change how people do business by making trust a prominent design attribute. By design, anything recorded on a Blockchain cannot be altered, and there are records of where each asset has been. So, while participants in a business network might not be able to trust each other, they can trust the Blockchain. The benefits of Blockchain for business are numerous and can viewed from three perspectives: benefits to transactions processing, benefits to finance and accounting teams, and benefits to third-party verification function.
As transactions volumes increase exponentially, the single biggest issue to contend with is verification of the validity of transactions in real time. A Blockchain network addresses this directly by virtue of the key characteristics of the platform:
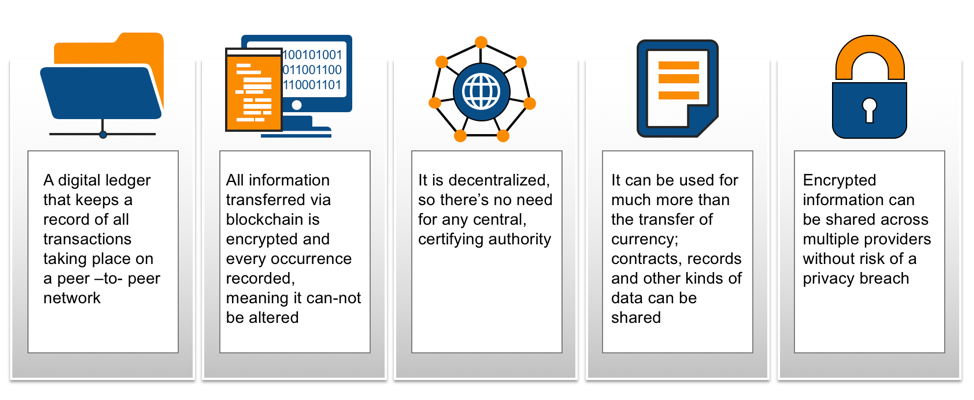
Image Licensed via Slide.net (through Nagendra Bangalore)
- Consensus – for a transaction to be valid and recorded on the platform, all participants must agree on its validity.
- Provenance – participants know where the asset came from and how its ownership has changed over time.
- Immutability – no participant can tamper with a transaction after it has been recorded in the ledger.
- Finality – A single, shared ledger provides one place to go to determine the ownership of an asset or the completion of a transaction.
Following on from the above, for finance and accounting teams, with an integrated distributed ledger accessed and updated by trusted participants, the benefits fall into:
- Decreased cycle time for initiating and completing transactions results in time savings and aids in improving working capital.
- Reduced cost of record keeping for transactions and assets, freeing up resources for other needs.
- Decreased fraud risk and the creation of real time compliance controls.
- Reduced monthly and annual general ledger closes and more accurate and timely financial reporting.
For third party verification and more specifically the independent audit function, an enormous advantage will be the ability to perform 100% audits (sampling will be a thing of the past) and third-party confirmations will likely be made redundant as information on the network is available in real time.
Smart Contracts and Integrating Artificial Intelligence
Two add-ons that provide greater functionality to the Blockchain platform are smart contracts and the use of artificial intelligence.
A smart contract is an agreement or set of rules that govern a business transaction; it is stored on the Blockchain and is executed automatically as part of a transaction. Smart contracts may have many contractual clauses that can be made partially or fully self-executing, self-enforcing, or both. Their purpose is to provide security superior to contract law while reducing the costs and delays associated with traditional contracts. As an example, for a solar energy supply contract, the solar operator may have bonus clauses contained in the Purchase and Sale Agreement for electricity generated over a target level. As energy is produced and data submitted to the network, once the target is breached the required invoice is generated for the operator and settled by the user without the need for human intervention.
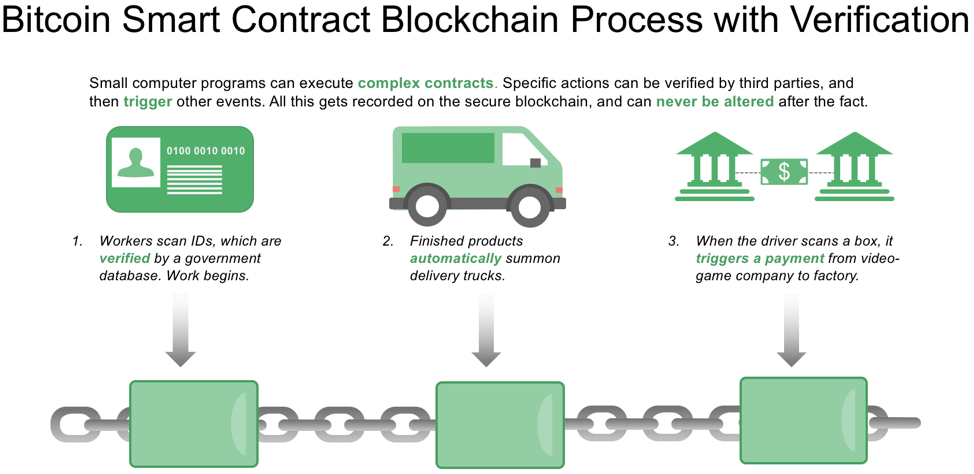
Image Licensed via Slide.net (through Nagendra Bangalore)
Blockchain networks will generate large volumes of data at the transaction level. Businesses will have access to a level of transactional data that was previously difficult to access without incurring significant time and cost. Finance teams will be able to use the power of Artificial Intelligence to mine this data to develop more accurate and targeted business models and make better decisions for the organization.
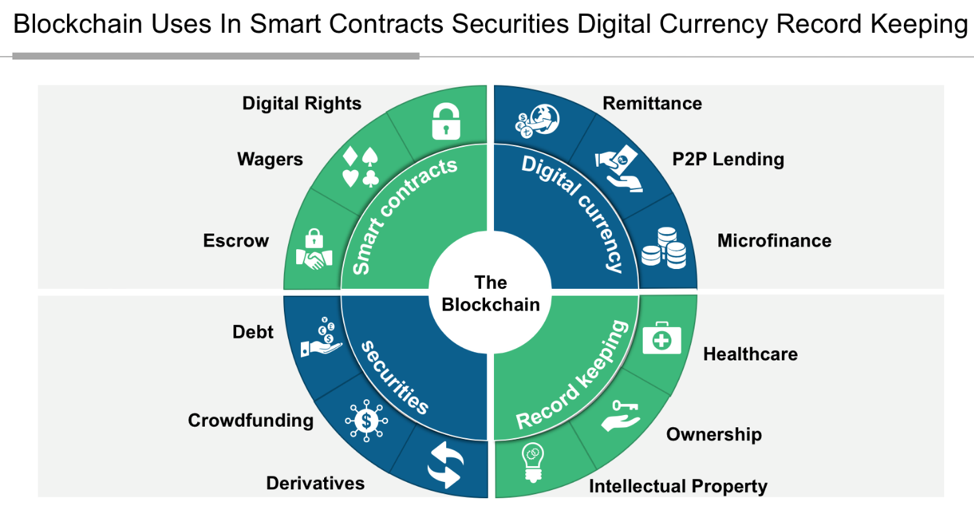
Image Licensed via Slide.net (through Nagendra Bangalore)
Vision, Strategy, and Execution
As leaders, you understand the importance of having a vision for your company’s future growth. With innovations in technology and the introduction of Blockchain to mainstream, it becomes imperative to assess your company’s readiness for the benefits offered by Blockchain.
As Vision evolves into Strategy, three strategy questions to carefully consider are:
- What Blockchain network and end stage implementation model is desirable for the organization?
- What is feasible for the organization given its current and future infrastructure needs?
- What is economically viable for the organization with regards to considerations 1 and 2 and the financial resources available to the organization?
Involvement of internal and external stakeholders in the deliberation of these questions should drive better accountability for the implementation project. A key question to carefully consider is whether to adopt a public or private Blockchain platform. Public platforms may not be the solution for all business networks, for example banks would not want public networks given the fiduciary responsibilities that must be met. In all business cases the likely model will involve setting up a permissioned network. With a permissioned Blockchain, each participant has a unique identity which enables the use of policies to constrain network participation and access to transaction details. Organizations simply cannot afford unauthorized access and use of their valuable data.
Execution should involve sound project management and experienced personnel. A mixture of internal personnel and outside consultants who are versed in Blockchain technology is desirable.
In closing, the rapid advances of technology on transaction processing, data security, and regulatory compliance will drive a paradigm shift of how companies manage their data and IT infrastructure. Embracing the value of Blockchain can be an effective solution.
Dwight Delapenha is the President and CEO of Fintech Global Consulting LLC, a firm providing consulting in the use and implementationof Blockchain technology.
